From Saptsandhu to Punjab: A civilisational journey
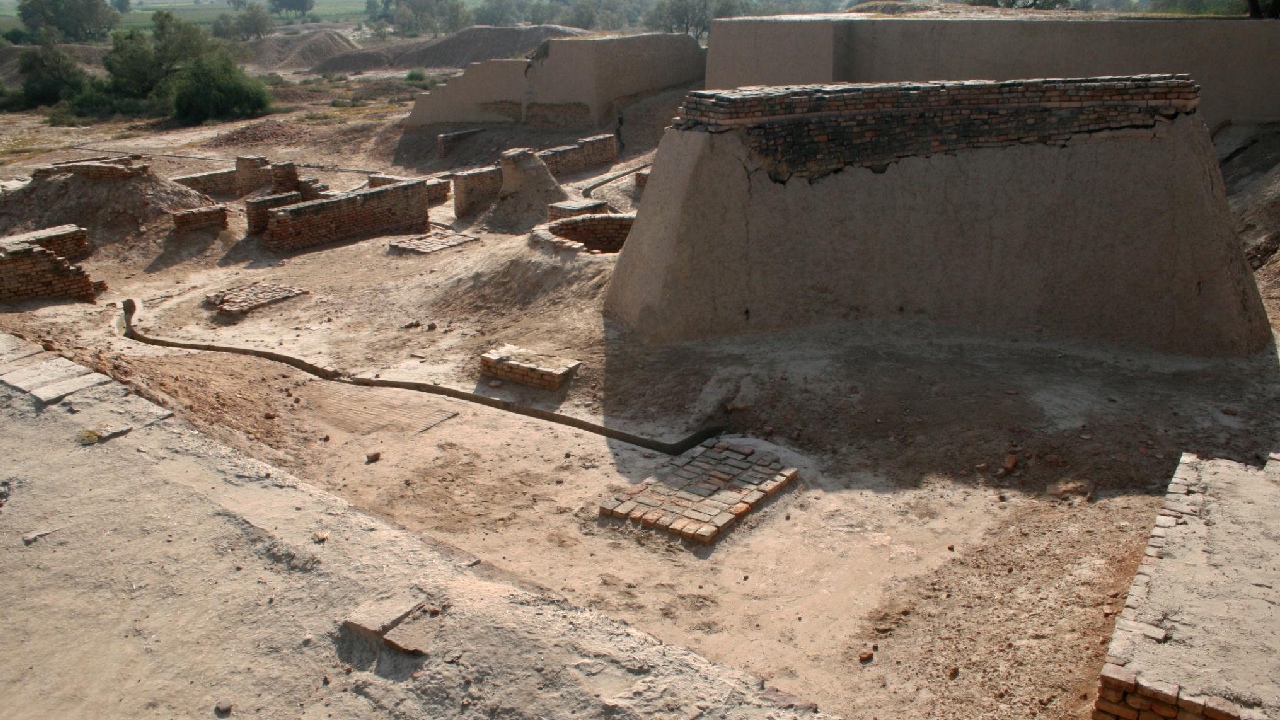

The Apeiron Legacy of Punjab traces its roots from the Indus Valley Civilisation and, having transited through various epochs had finally attained its present entity -The Punjab. It is worth taking a look at the interesting journey spanning various eras and generations. Originally named as "Sapta Sindhu" during the "Rig Veda Period" (1500-1000 years BCE), means, the land of seven rivers, these were: Sindhu, Vitasta(Jhelum), Asikni (Chenab), Parusani (Ravi), Vipasa (Beas), Shatudari (Satluj) and Saraswati. It is believed that during the Vedic Period (1000-500 years BCE), the Saraswati River, flowing between Yamuna and the Satluj Rivers, had started drying up and towards the end of this Period, it finally disappeared. Also, the Indus River was de-linked, hence, the Sapta Sindhu, left with five rivers, was rechristened as "Panchnaad" (land of five rivers) during 500-300 years BCE.
The early indications of spoken language had first come from the "Mid Indo-Aryan Period" (600 BCE- 1000 CE), and were known as the Prakrit language. With successive refinements, its improved version that finally came out was called "Apbhransh" (mixed ). The historical annals suggest that towards the end of 10th century CE, it led to the creation of Hindi, Panchnaad (Punjabi) and various South Asian dialects. Alongside, the "Sharda Script"- the mother of all was developed during the 8- 9th Centuries CE. It was named after the ancient University and Centre of Learning at Sharda Shakti Peeth (located in Kashmir in Keran Sector close to the LOC in POK) which played a crucial role in its development and popularisation. It led to the creation of a mélange of scripts and one of them was "Landa Script". Primarily known as the Merchants' Script , it was also used for literary and administrative purposes and was soon adopted by Panchnaad language.
Around this period "The Nath-Yogi" Sect was launched by Saint Matsendranath aka Machhindernath, his teachings and the spiritual disciplines were profoundly discoursed in Panchnaad by his disciple- Yogi Gorakhnath further buttressed the spread of local dialect.
In 14th Century, two historic events took place. One, the Sufi Saint Amir Khusro in order to bridge the gap between the two contrasting morphemes, the Sanskrit predominant Hindi and the Persian, evolved a new lexicon named as "Zubane Ordu ( Urdu) written in Persio Arabic Script.
It soon achieved mass acceptability and was monikered as "Shahmukhi Script" in the North and the North western regions and was subsumed as the primary script by the Panchnaad language. Two, Iban Battuta, a Maghrebi (North African) an explorer from Morocco, arrived in India in 1334 and stayed till 1342. During his sojourn, it is learnt that he had changed the name of Panchnaad with the Persian epithet - Punjab; the same had been documented in his Book- Rihla
(travelogue). Axiomatically, its language, hereafter was known as the Punjabi. Concomitantly, the Sufi Cult led by Sheikh Farid had made its mark in Punjab, subsequently pursued by Bulle Shah, Waris Shah, Shah Muhammed, Shah Hussain, Damodar Das Arora from Jhang ( the original Writer of Folk Tale Heer-Ranjha) and alike, by preaching and spreading the Sufi philosophy in Punjabi had rendered a great service to the people and the culture of recently christened Punjab. Yet another monumental event was awaiting, the origin and spread of Sikhism and its preachings during 15th to 18th century marked an Era of spiritualism, consecration, social oneness and bonhomie amongst Punjabis. It was during this period, the Punjabi got its captive script, the Gurmukhi, devised by Second Guru, Sh Guru Angad Dev ji.
During the Mughal rule, amongst others, in order to refine and streamline the administrative set up, Raja Todar Mal, the Financial Virtuoso in Akbar's regime, subdivided Punjab into five Doabs (area between two rivers) and acronymed them from the names of the rivers binding the Doabs.
Starting from East; the area between Satluj and Beas Rivers was called Bist Doab (Jallandhar Hoshiarpur), the territory bound by Beas and Ravi Rivers was named Bari Doab ( also called Majha, Amritsar, Lahore), the area between Ravi-Chenab Rivers was named Rachna Doab (Faislabad, Sialkot), the belt demarcated by Chenab and Jhelum Rivers was called Jhajj Doab ( Sargodha,Gujarat), and finally, the Western-most was Sind Sagar Doab between Jhelum and the Indus Rivers ( Rawalpindi, Chakwal).
Maharaja Ranjit Singh's rule from 1801-39 is best remembered for the social, religious, political and the egalitarian reforms. The gloaming of Sikh empire came after the Second Anglo Sikh War 1848-49 followed by the annexation of Punjab by the British in April 1849. After consolidating their hold, the Britishers took upon the task of improving the irrigation and the cultivation in Punjab.
It underwent three major partitions, the first one in 1901 when the NWFP was taken out followed by Delhi becoming the Capital Territory in 1911 and finally the cataclysmic schism in 1947 which dissected the State — the East and the West Punjab!
Col Ramesh Davesar is a Veteran who fought 1971 Indo-Pak War; had two years stint in the IPKF & commanded Battalion in the Valley; views are personal